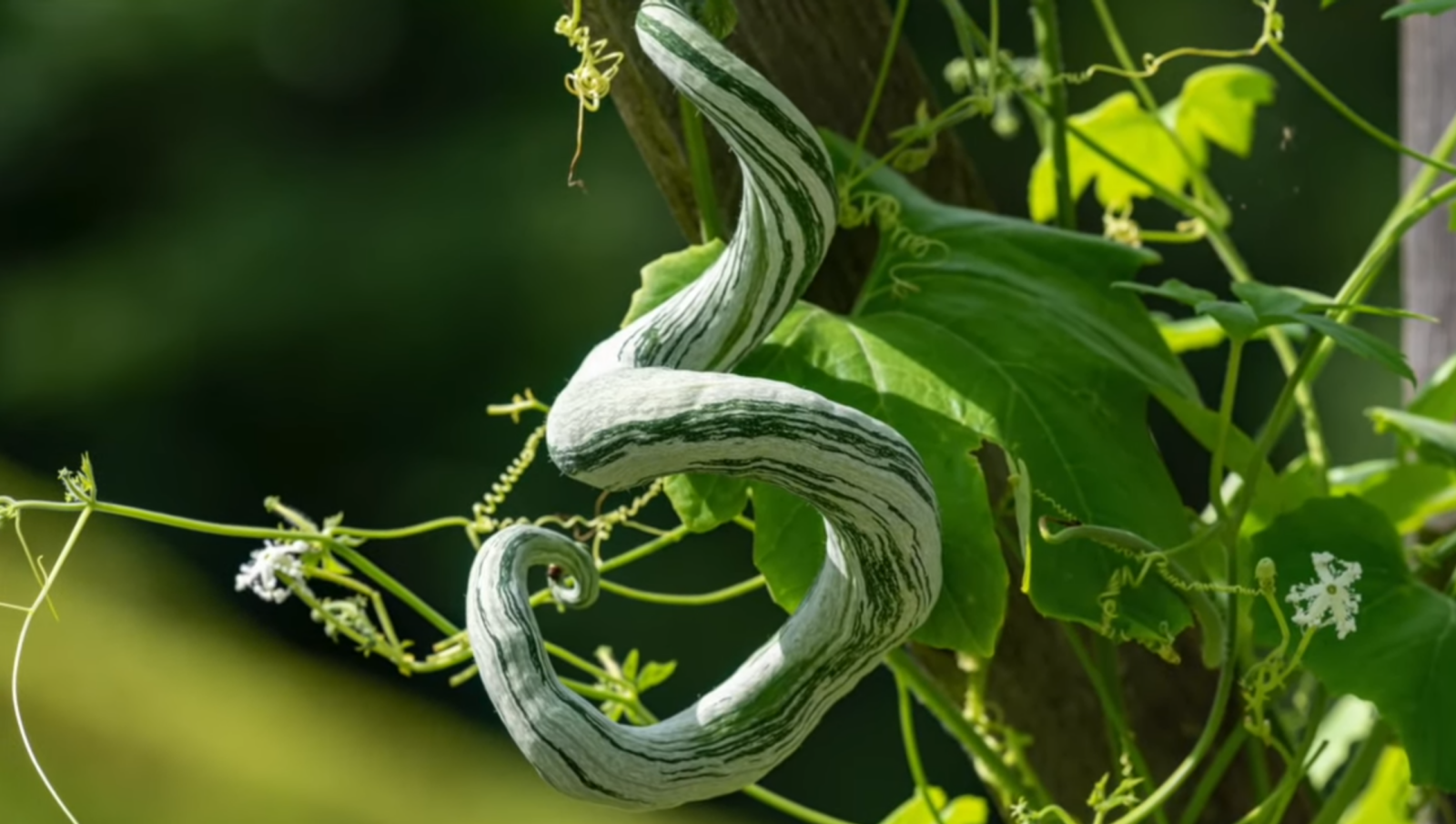
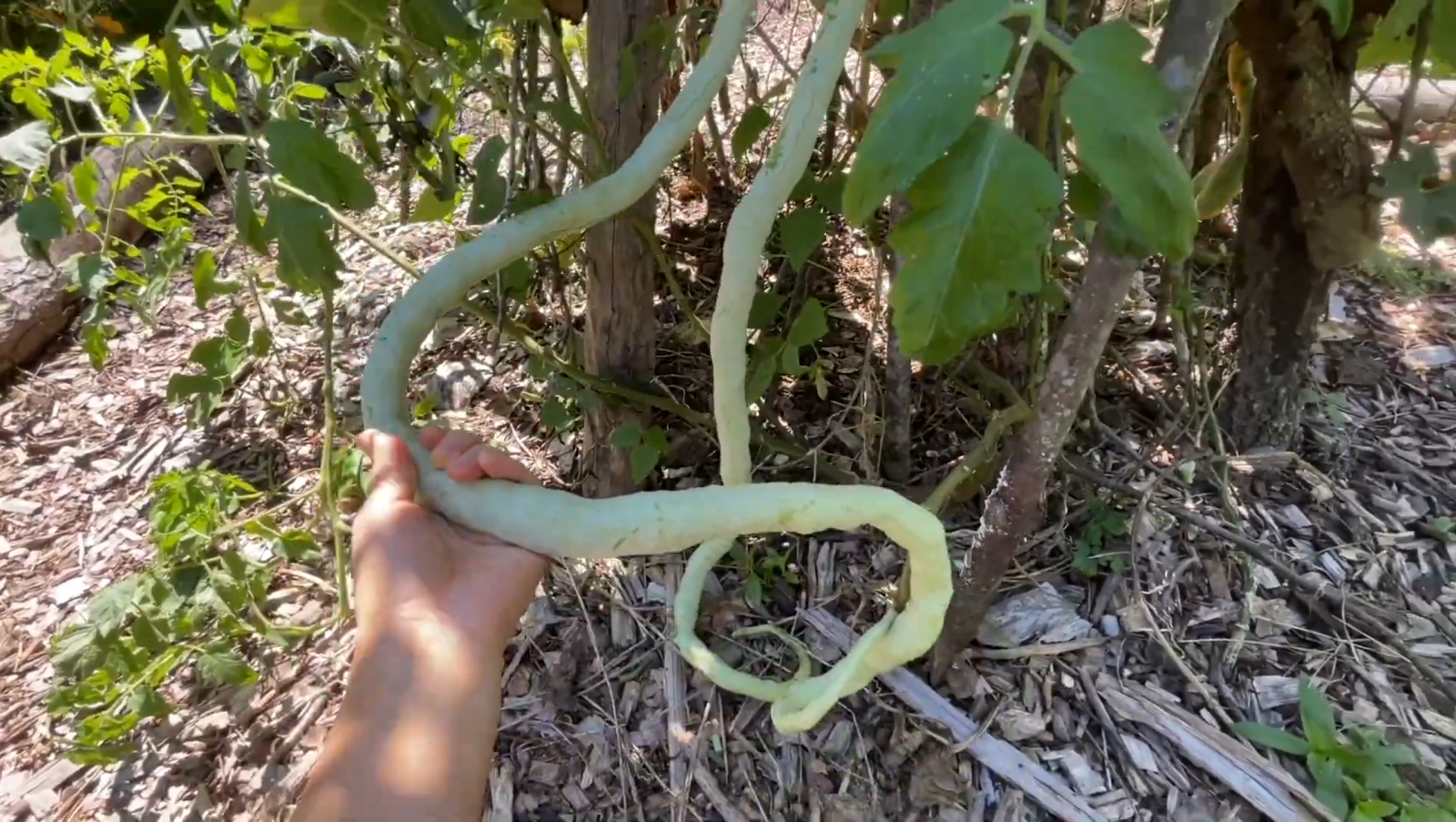
The Python Snake Bean, also known as Trichosanthes cucumerina, Indian Python Snake Bean and Chinese Python Snake Bean, is an intriguing and delicious addition to any garden, with its serpentine shape often catching the attention of visitors. Despite its appearance, this unique vegetable is neither a snake nor a bean. Instead, it is a member of the gourd family and has quickly become a favorite among gardeners for its tender and flavorsome qualities when picked young, resembling a superior green bean.
Table of Contents
ToggleOriginating from southern and eastern Asia, as well as the western Pacific Islands, the snake bean is believed to have been domesticated in India. Its scientific name, “Trichosanthes,” translates to “hairy flower” in Greek, aptly describing the delicate and fragrant flowers that bloom on the vine at night. Due to its extensive geographic distribution, the snake bean is known by various other names, such as snake gourd, Serpent Gourd, Chichinga, Padwal, and Snake Tomato.
Although relatively unknown in U.S. markets due to its shape making it difficult to pack and ship, the snake bean is a key player among Chinese vegetables, which encompass over 150 species of wild and cultivated cucurbits. The Chinese Green Python variety stands out, as it can grow to over five feet long and one-and-a-half inches in diameter.
As the snake bean matures, it develops a bright green, waxy exterior. To enjoy its best flavor, harvest the vegetable when it’s about one or two feet long. It can be stir-fried with peppers and onions for a traditional dish or used as a substitute for green beans and summer squash in various recipes. The red, fleshy pulp surrounding the seeds of ripe snake beans is an excellent alternative to tomato paste.
The Python Snake Bean is a staple in Indian and Asian cuisines and has gained popularity among African gardeners. Commercial growers in East African urban centers have started cultivating Indian snake bean varieties as a specialty crop. This nutritional powerhouse is rich in antioxidants like Vitamin E and Vitamin C, essential minerals such as potassium, phosphorus, and calcium, and offers high levels of fiber and protein.
In addition to its culinary uses, the snake bean has long been a part of folk medicine, employed in the treatment of headaches, fever, inflammation, and digestive issues. The South Asian traditional medical systems of Ayurveda and Siddha medicine hold it in high esteem.

Growing Python Snake Bean in Your Home Garden: A Comprehensive Guide
If you’re a home gardener looking to grow the Python Snake Bean, follow these helpful tips and guidelines to ensure optimal growth and a bountiful harvest.
Soil Requirements
Python Snake Beans thrive in well-draining, fertile soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 6.8. To achieve the best results, prepare your garden bed with a mixture of compost or well-rotted manure to enrich the soil and improve its structure. If your soil is clay-based or tends to retain water, consider adding sand or organic matter to enhance drainage.
Optimal Growing Conditions
Python Snake Beans are heat-loving plants and require full sun for optimal growth. They need a minimum of 6 to 8 hours of sunlight daily. These beans are sensitive to cold, so it’s crucial to plant them when the soil temperature has reached at least 60°F (16°C) and all danger of frost has passed. The ideal temperature range for growth is between 75°F and 85°F (24°C to 29°C).
Planting Timeline
- Seeds preparation (2-3 days before planting): Soak the seeds in water for 24 hours to expedite germination. After soaking, place the seeds between moist paper towels and store them in a warm, dark place for another 24 to 48 hours until they sprout.
- Planting (Late spring/early summer): When the soil temperature has reached at least 60°F (16°C) and there’s no risk of frost, sow the pre-soaked seeds directly into the prepared garden bed. Plant the seeds about 1 inch deep and 12 inches apart, with rows spaced approximately 3 feet apart. If you’re growing the beans on a trellis, plant the seeds about 6 inches away from the base of the structure.
- Germination (1-2 weeks): In ideal conditions, Python Snake Bean seeds will germinate within 7 to 14 days. Keep the soil consistently moist during this period, but avoid overwatering, as it can lead to rot.
- Climbing and trellising (3-4 weeks after germination): As the plants grow, they’ll begin to climb any nearby structures. Train the vines onto a sturdy trellis, pergola, or fence to provide adequate support. Encourage climbing by pinching off the lowest-growing side shoots and branches.
- Flowering (4-6 weeks after germination): Python Snake Beans will start producing delicate, fragrant flowers about 4 to 6 weeks after germination. Ensure the plants receive consistent moisture, but avoid wetting the flowers, as this may reduce pollination.
- Harvesting (6-8 weeks after germination): The beans will be ready to harvest approximately 6 to 8 weeks after germination, depending on the growing conditions. Harvest the snake beans when they are about 1 to 2 feet long for the best flavor and tenderness. Regularly picking the beans will encourage continuous production throughout the growing season.
Watering and Fertilization
Python Snake Beans require consistent moisture throughout their growth cycle, particularly during flowering and fruit development. However, avoid overwatering, as it can cause root rot. Drip irrigation or soaker hoses are recommended to maintain even moisture without wetting the foliage and flowers.
Apply a balanced, slow-release fertilizer at planting and again when the plants start to flower. Alternatively, side-dress with well-rotted manure or compost throughout the growing season to provide consistent nutrients.
Pest and Disease Management
Python Snake Beans may attract common garden pests like aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites. Regularly inspect your plants and use organic pest control methods, such as insecticidal soap or neem oil, to manage infestations. Encourage beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings to help keep pest populations in check. These beans are generally resistant to diseases, but proper spacing, adequate air circulation, and consistent moisture management will help prevent issues like powdery mildew and leaf spot.
By following these guidelines and closely monitoring your Python Snake Bean plants, you’ll enjoy a rewarding and bountiful harvest. Not only will you have an intriguing addition to your home garden, but you’ll also be able to savor the unique flavors and nutritional benefits this remarkable gourd has to offer.
The Python Snake Bean is not only a great addition to your garden for its nutritional and medicinal properties, but it’s also a fun plant to grow, particularly in a children’s garden. Its unusual shape and appearance can make for some amusing moments with unsuspecting visitors!