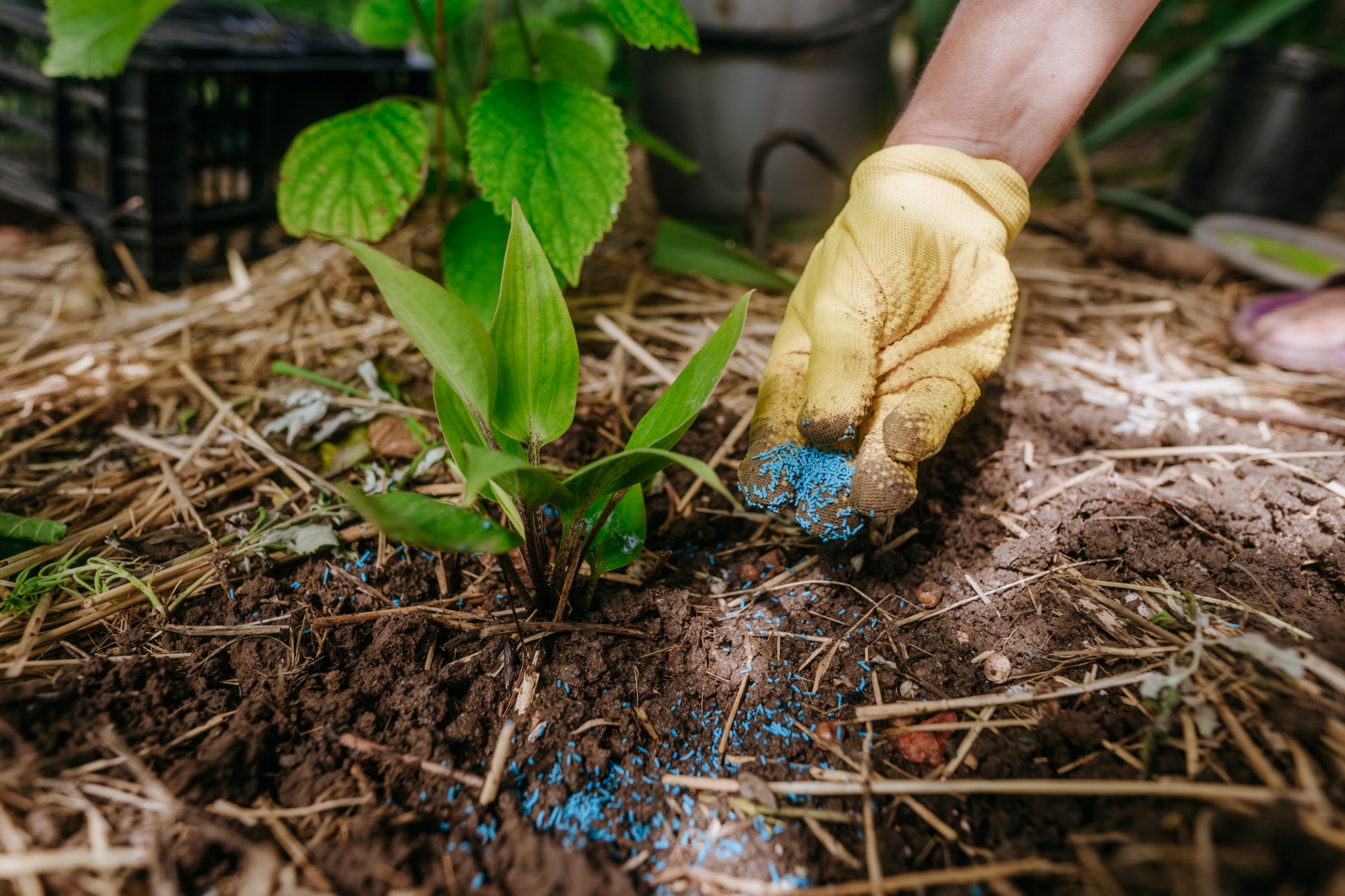
Hey gardeners! Have you been wondering when to apply fertilizers to your vegetable plants? In this article, I’ll discuss the best time to utilize fertilizers on different types of vegetables throughout the growing season, tips on how much fertilizer should be applied, and other key considerations. Let’s jump right into demystifying when and how fertilizer should be applied for various veggie crops.
Table of Contents
ToggleTypes Of Fertilizers
When it comes to fertilizing vegetables, there’s a lot of options out there – and the right one depends on what plant you’re growing. Fertilizer is basically any substance that helps provide nutrients to plants. It can be organic or synthetic and come in many forms: granular, liquid, slow-release tablets, etc.
Organic fertilizer is made from natural ingredients like composted manure or decomposed leaves. This type of fertilizer works slowly over time and provides both major and trace elements for your vegetable garden. On the other hand, synthetic fertilizer consists of chemical compounds such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK). Synthetic fertilizers are fast-acting and release their nutrients quickly into the soil.
No matter which kind you choose, make sure it has all three macro-nutrients—nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K)—in balanced amounts so your veggies get exactly what they need for optimal growth. Now that we’ve understood the types of fertilizers available let’s turn our attention to soil requirements…
Soil Requirements
When fertilizing vegetables, it is important to meet the soil’s requirements. This means understanding what type of soil your vegetable plants need to thrive.
There are four key considerations when evaluating soils for a vegetable garden:
- Soil texture – this includes sand, silt and clay content
- Soil pH – acidic or alkaline levels which can be adjusted with lime if needed
- Nutrient availability – nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen must be present in adequate amounts
- Organic matter content – organic matter helps retain water and improve soil structure
With these elements taken into consideration, you should have an idea of whether your soil needs additional amendments such as compost or fertilizer before planting vegetables. Next we’ll discuss application timing once the soil has been prepared appropriately for growing vegetables.

Timing Of Application
Having discussed the necessary soil conditions for healthy vegetable growth, it is essential to consider when to apply fertilizers. Like a conductor conducting an orchestra, timing is key in ensuring that nutrients are delivered at just the right moment to maximize plant growth and yield.
| Time | Best Fertilizer Type |
|---|---|
| Spring | Slow-release fertilizer |
| Early Summer | High Nitrogen liquid or granular fertilizer |
| Late Summer/Autumn (depending on climate) | Balanced slow-release fertilizer with additional iron sulphate |
In spring, applying a slow-release fertilizer gives your vegetables a steady nutrient supply throughout the growing season. This type of feed should be applied yearly before planting seeds or transplanting seedlings as it will stay active in the soil for up to 8 months – providing long-lasting nutrition without risk of overfeeding. In early summer, a high nitrogen liquid or granular fertilizer can help stimulate new foliage growth and flowering production during this important period of rapid vegetative development. Finally, late summer into autumn requires a balanced slow-release fertilizer which contains extra iron sulphate; ideal for root crops such as carrots and beetroot which require more phosphorus than nitrogen but still benefit from trace elements found within the feed.
By understanding when to apply different types of fertilizers you can ensure your vegetables receive optimum levels of nourishment throughout their entire life cycle. The next step on our journey is uncovering how much fertilizer needs to be used…
Amount To Use
When it comes to applying fertilizer to vegetables, the amount used is important. Too much can burn and damage plants while too little won’t provide enough nutrients for the plant to thrive. The type of vegetable will also determine how much should be applied; some require more than others.
Most vegetables need about 1/4 cup of a complete 10-10-10 fertilizer per 25 square feet of garden space. If using an organic fertilizer such as composted manure or fish emulsion, double that amount because these fertilizers are not as concentrated as chemical ones. When applying dry fertilizers, rake into the top one inch of soil around each plant and water well afterwards.
Mix 2 tablespoons of a balanced 10-10-10 formula for container gardens with 1 gallon of potting soil when planting seedlings in containers or hanging baskets. For established plants, dissolve one teaspoonful of 20-20-20 liquid concentrate in a quart of water and apply once every two weeks throughout the growing season. Be sure to follow package instructions carefully and never use more than recommended amounts—a little goes a long way!

Frequently Asked Questions
What Types Of Vegetables Should I Use Fertilizer On?
When it comes to vegetable gardening, choosing the right fertilizer can be a challenging task, as different types of vegetables have varying nutrient requirements. Different types of vegetables require different amounts and kinds of fertilizer; for instance, tomatoes may need more nitrogen than cucumbers or squash. Additionally, some vegetables such as root crops like potatoes or carrots don’t usually require any additional fertilization since they get their nutrients from deeper layers in the soil. Choosing a fertilizer that provides the right balance of nutrients is important to support healthy growth and development.
To get you started, here are some different types of popular vegetables and their key nutrient requirements:
| Vegetable | Key Nutrients |
|---|---|
| Tomatoes | Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium |
| Carrots | Phosphorus, Potassium |
| Cucumbers | Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium |
| Lettuce | Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium |
| Peppers | Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium |
| Broccoli | Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium |
| Beans | Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium |
| Onions | Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium |
Remember that vegetables’ nutrient requirements may vary depending on the specific cultivar or variety being grown. Additionally, soil type and pH can also influence nutrient availability, so conducting a soil test to determine any deficiencies or imbalances in nutrient levels may be helpful before selecting a fertilizer.
How Often Do I Need To Apply Fertilizer To My Vegetables?
When it comes to applying fertilizer for vegetables, timing is key. Generally speaking, most vegetable gardens will benefit from an application of fertilizer once every two weeks during the growing season. You might bump into some exceptions depending on the type of vegetables you’re growing and their specific needs. For example, leafy greens may require more frequent fertilizing than root crops.
That being said, it’s important to remember that you should always follow package directions when using any commercial fertilizer product and pay attention to signs that your soil might need additional nutrients such as yellowing leaves or lack of growth. If this happens, you can adjust your schedule accordingly.
Is It Safe To Use Fertilizer On Organic Vegetables?
Using fertilizer on organic vegetables is generally considered safe, but it depends on the fertilizer being used. Organic fertilizers, such as compost and manure, are made from natural materials and are generally considered safe for use on organic vegetables. It’s important to carefully read and follow the instructions on any fertilizer you use, and to avoid using synthetic fertilizers that contain harmful chemicals.
Using a synthetic fertilizer doesn’t necessarily mean that your produce isn’t organic, but it does depend on the certification standards being followed. In general, organic farming practices prioritize the use of natural fertilizers like compost and manure and minimize the use of synthetic fertilizers. For example, the USDA organic certification program has specific guidelines for what types of fertilizers can be used in organic farming, and synthetic fertilizers are generally only allowed under specific conditions and restrictions.
However, synthetic fertilizers alone don’t automatically disqualify produce from being considered organic. Some organic certification programs or standards may allow for the limited use of certain types of synthetic fertilizers under certain circumstances, such as when natural sources of nutrients are insufficient. Ultimately, whether or not produce is considered organic depends on the specific certification standards being followed and the practices used by the farmer.
What Are The Environmental Impacts Of Using Fertilizers On Vegetables?
Using fertilizers on vegetables can have a wide range of environmental impacts. To start off, let’s take a look at how fertilizer use affects soil health. Chemical fertilizers add essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium which help plants grow faster and stronger. However, if applied excessively or incorrectly, the chemicals may leach into nearby water sources such as streams or lakes where they can cause serious damage by killing aquatic life or creating oxygen-deprived dead zones. Additionally, overuse of chemical fertilizers can lead to nutrient build-up in soils that creates an imbalance detrimental to long-term sustainability.
It’s also important to note that chemical fertilizers aren’t just limited to their effects on soil health; other issues arise from their production and distribution as well. Fertilizer production requires large amounts of energy and resources which contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and pollution across the globe. The transportation of fertilizer adds another layer of environmental impact due its contribution towards air pollution and climate change while burning fossil fuels during transit.
Over to You!
Think of yourself as a gardener taking care of your plants like children – applying just enough nourishment but not too much or too little so that they will grow healthy and strong. The same goes for feeding your vegetable garden! If done properly, adding fertilizer gives you greater control over the yield and quality of your harvest, bringing delicious rewards when done correctly.
Overall, using fertilizers on vegetables requires careful consideration for the best results. With some time and effort put towards understanding which types are best suited for different vegetables and being mindful of environmental impacts caused by its production process, you’ll be well-equipped with the knowledge to help give your veggies just the right amount of nutrition needed to flourish!